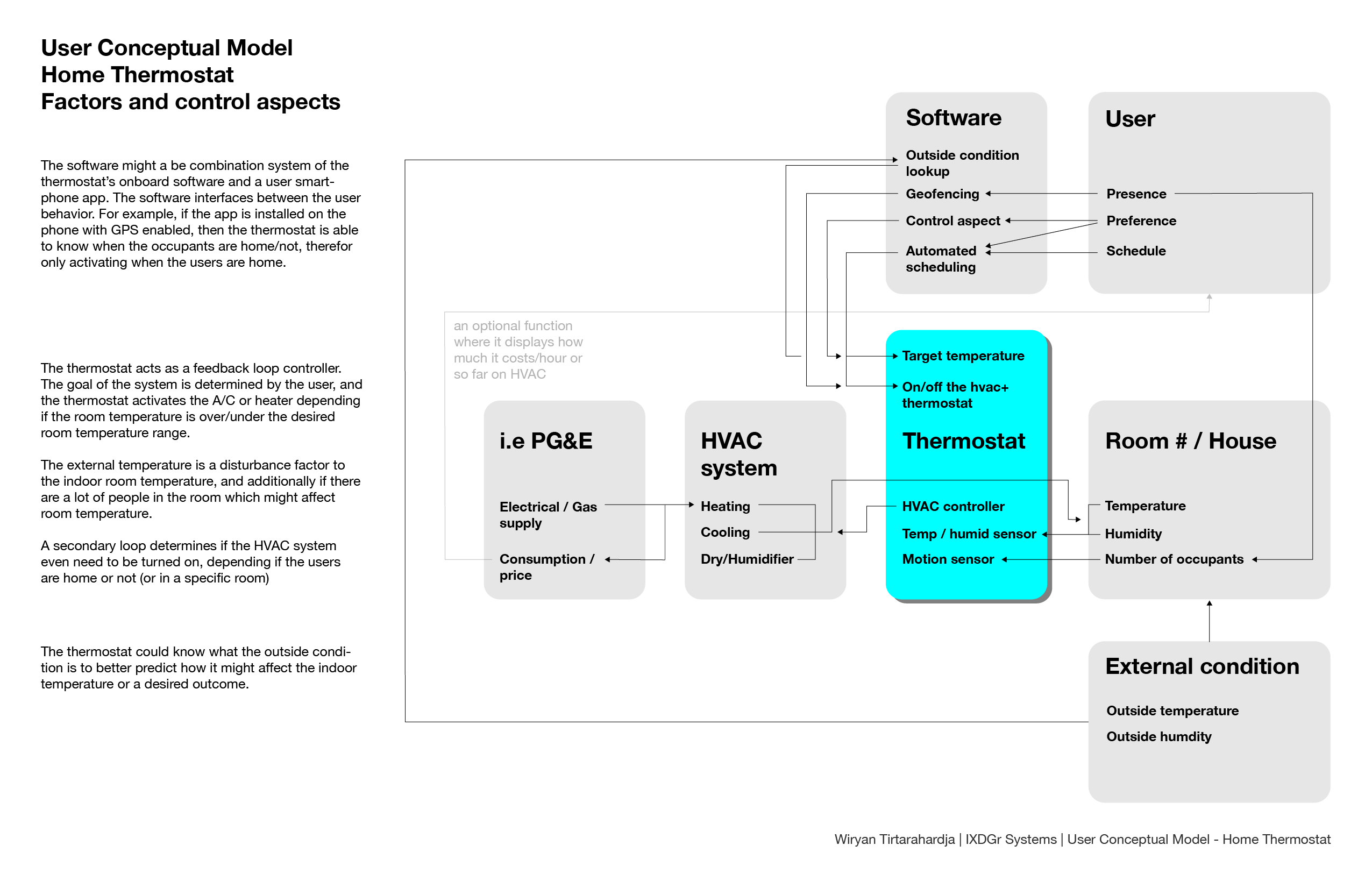
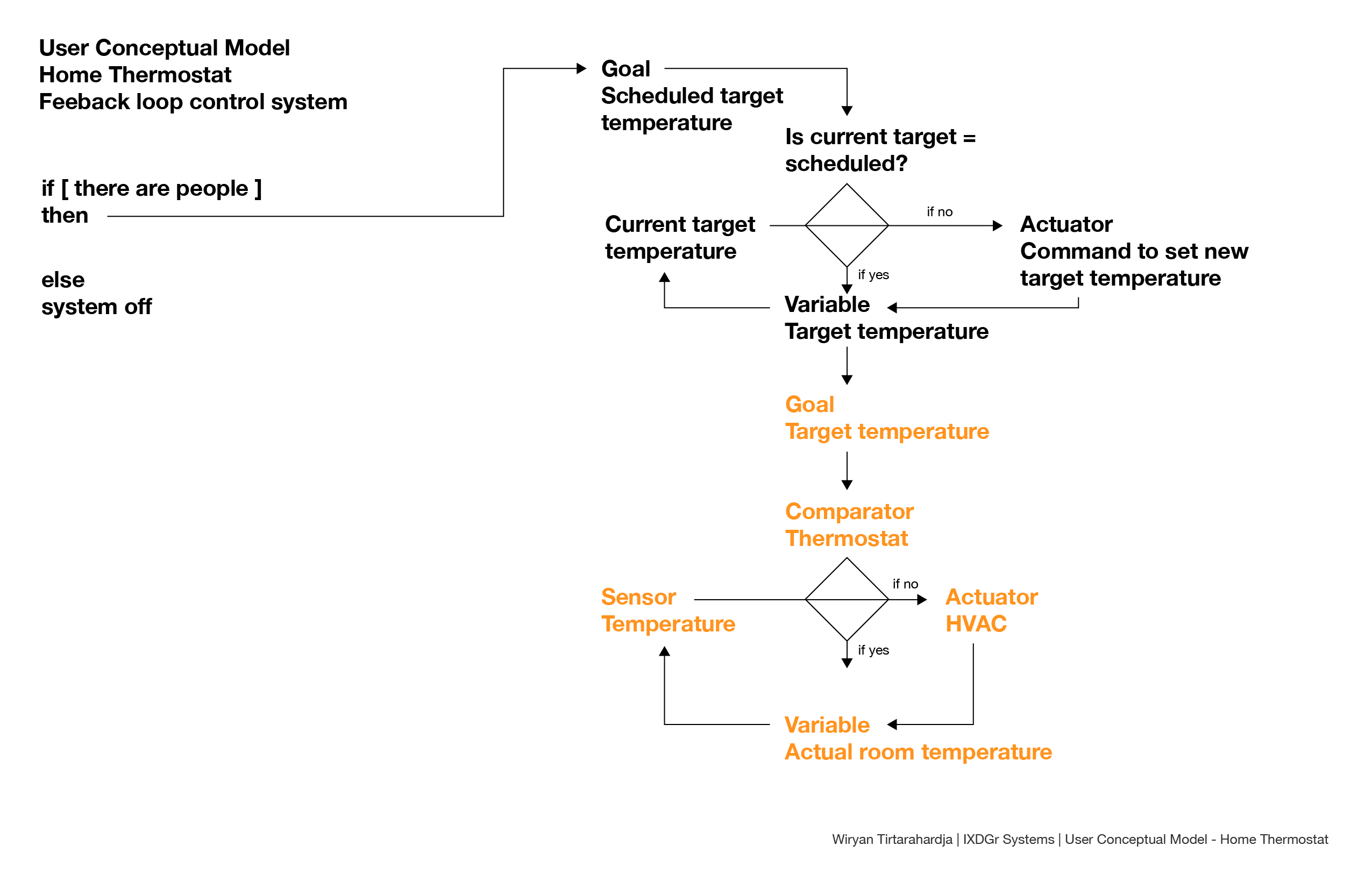
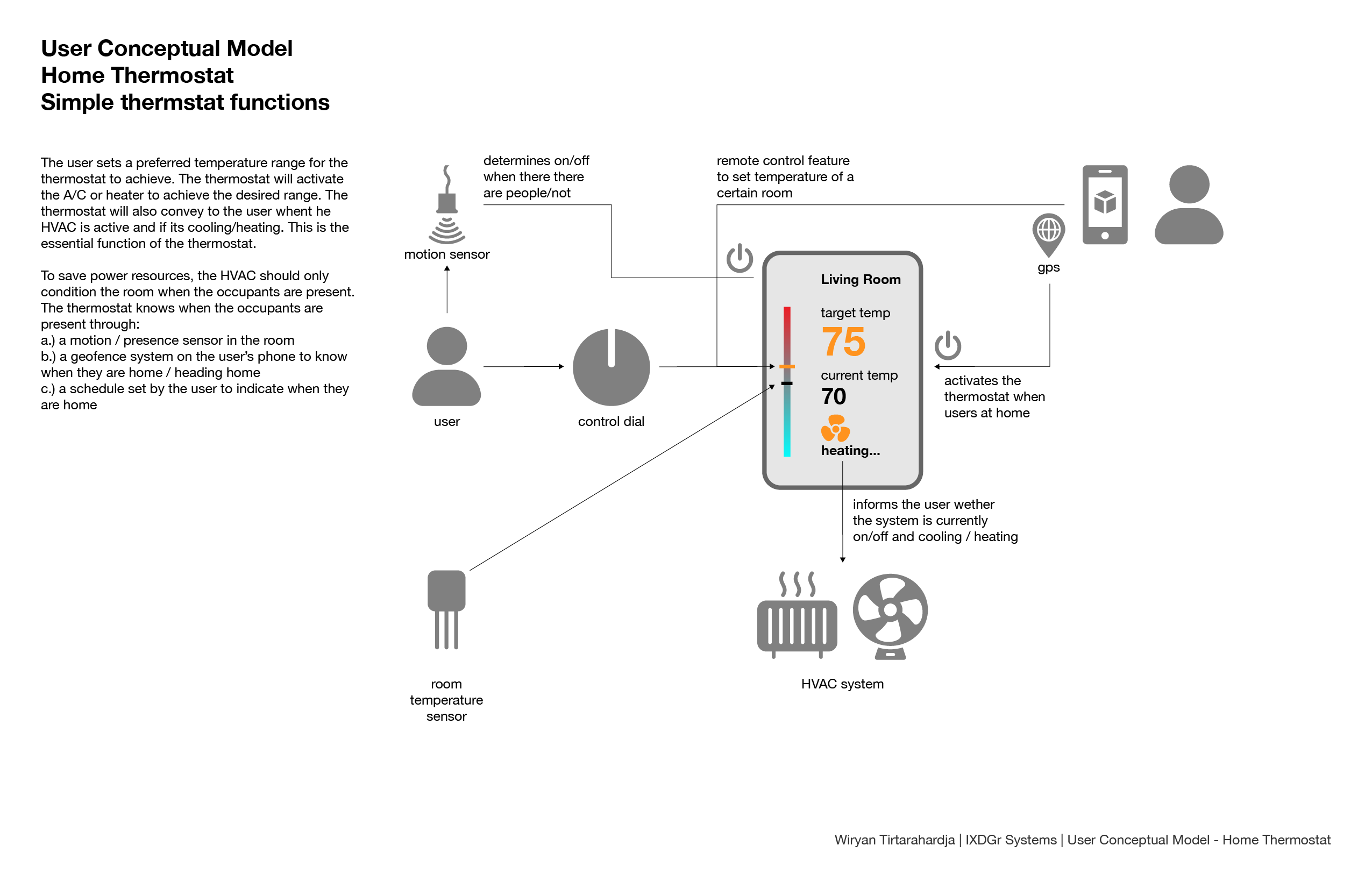
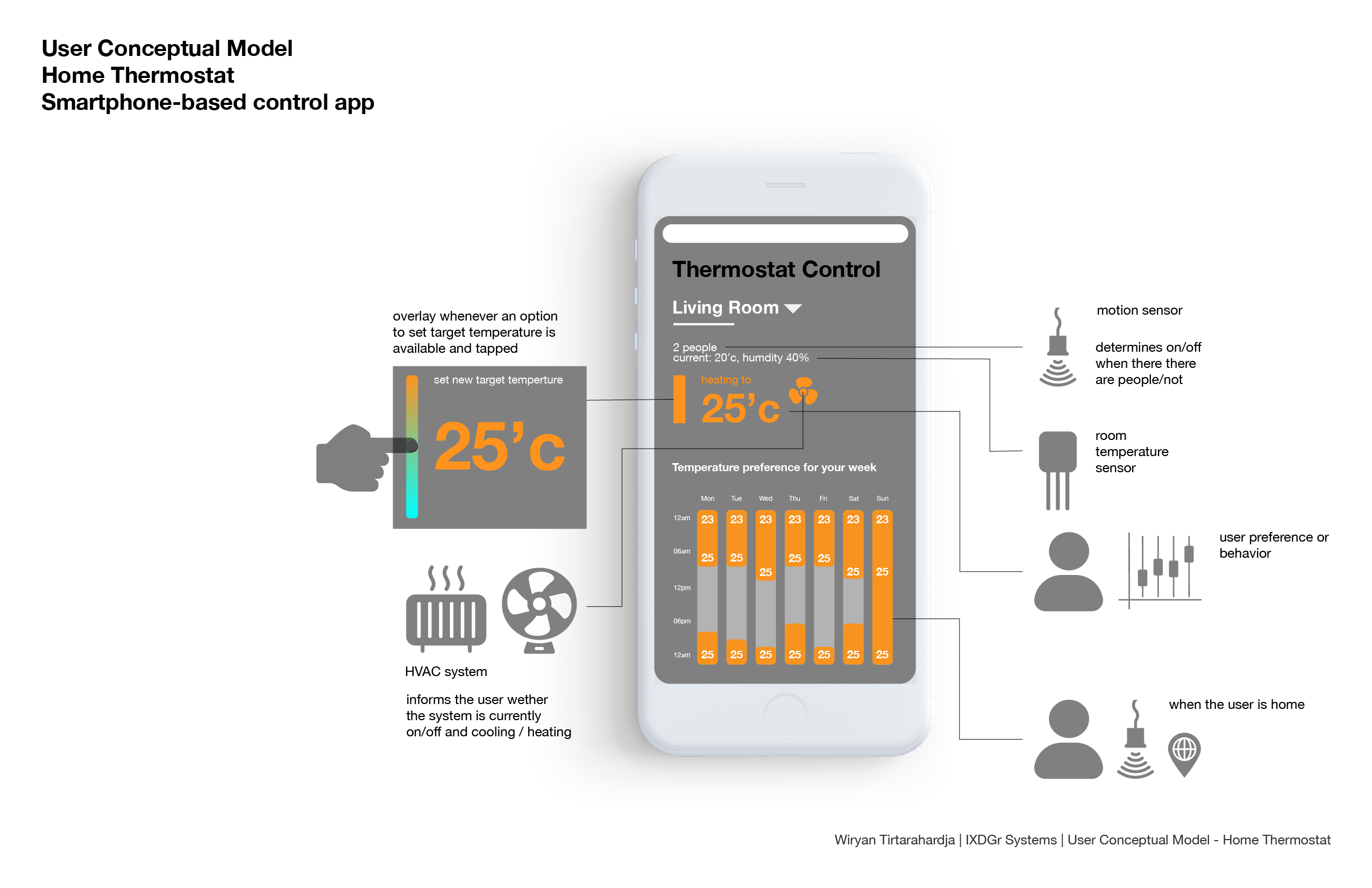
Application model: image processors
Above is a simplified visualization of how raster-based image processors work and how they write and store information. Essentially, the canvas is divided into a grid depending the pixel count (which is the size of the canvas). Each pixel is given a set of hexadecimal numbers which indicate the color value. Information is saved in the file in a similar way, with the header and footer indicating the information of the file (i.e file type, size, metadata), and the meat of the file which is said hexadecimal values.